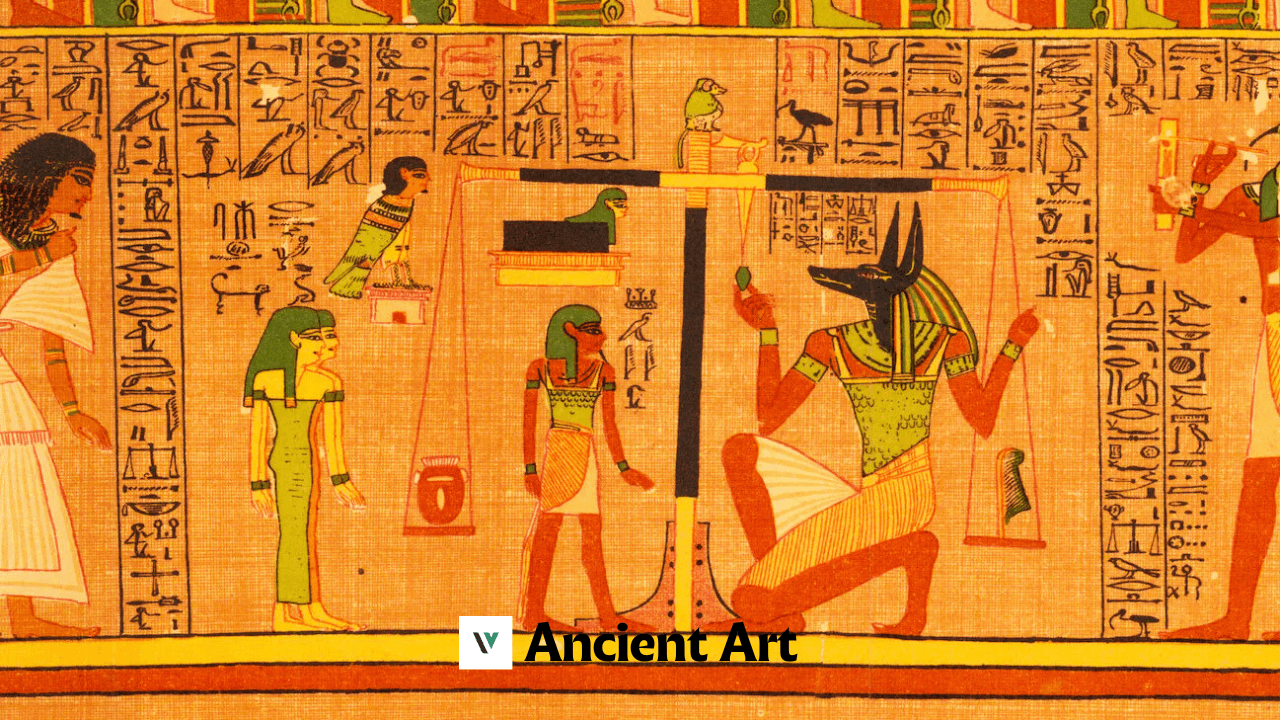
The domain of ancient art gives an intriguing window into the set of experiences, cultures, and convictions of former civilizations. By looking at ancient art, we can follow humankind’s development from crude articulations to refined structures, exhibiting an excursion that traverses millennia. Ancient art not only fills in as a record of human accomplishment but also keeps on moving current workmanship, making it genuinely immortal. This article investigates the meaning of antiquated workmanship, its unmistakable structures, striking civic establishments that added to its turn of events, and the methods utilized in making these magnum opuses.
Understanding Ancient Art
Old Workmanship, by definition, envelops visual manifestations from the earliest times up to generally the fall of the Roman Domain in the fifth century CE. This period saw the introduction of a portion of humankind’s earliest imaginative undertakings, going from simple cavern works of art to fantastic figures and engineering. ancient art’s immortal nature lies in its capacity to convey the contemplations, convictions, and feelings of early social orders through symbolism, plan, and structure.
The significant objective of old workmanship was tasteful delight as well as utilitarian purposes. Numerous old fine arts were utilized for strict, political, and social customs. A few fine arts were made to respect the divine beings, commend rulers, or act as images of influence and riches, while others portrayed regular day-to-day existence and the climate.
The Origins and Forms of Ancient Art
The excursion of ancient art started with the principal human-made blemishes on cave walls. The works of art that were created over centuries incorporate cavern canvases, figures, earthenware, mosaics, and materials. Each structure offers knowledge of the social and cultural upsides of old human advancements.
- Cave Paintings and Petroglyphs: These are among the earliest types of ancient art, tracing back to ancient times. Early people utilized normal colors to make pictures of creatures, hunting scenes, and unique images on cave walls. Well-known models remember the cavern artworks of Lascaux for France and Altamira in Spain, which give proof of early imaginative articulation and the representative idea of ancient people groups.
- Sculpture: Antiquated models shifted from little dolls to monster sculptures, addressing divine beings, rulers, and fanciful creatures. Early models incorporate the Venus puppets, which date back to the Paleolithic time and are accepted to address richness. Afterward, the sculptural works of the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans accomplished a degree of naturalism and magnificence that keeps on being praised.
- Pottery and Ceramics: Ceramics filled not just pragmatic needs for putting away food and fluids but additionally had beautifying components. Antiquated ceramics frequently included multifaceted plans, portraying stories, legends, and scenes from day-to-day existence. The Greeks, for example, are famous for their painted jars that show itemized fanciful, and verifiable scenes.
- Mosaics and Frescoes: Mosaics, produced using little shaded stones or glass pieces, decorated floors and walls in antiquated civilizations like the Romans and Byzantines. Frescoes, which included painting on wet mortar, were one more conspicuous type of enrichment, utilized broadly in antiquated Rome and Minoan Crete.
- Textiles and Metalwork: Albeit fewer models have been made, materials and metalwork were additionally critical types of Old Workmanship. Early developments like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians delivered finely woven textures and complicated adornments, delineating their creative ability and social qualities.
Ancient Egyptian Art: A Glimpse into the Divine
The specialty of antiquated Egypt is maybe one of the most notorious instances of ancient art. With a set of experiences that traverses north of 3,000 years, Egyptian craftsmanship served an essentially strict and funerary capability. The Egyptians put stock in existence in the wake of death and utilized craftsmanship to get ready for the excursion into the following scene.
- Statues and Temples: Egyptian workmanship was described by unbending, adapted structures that portrayed divine beings, pharaohs, and significant figures steadily. Sculptures and sanctuary carvings were made to respect the divinities and rulers, who were many times portrayed as awesome figures.
- Tomb Paintings and Reliefs: The burial places of pharaohs and aristocrats were decorated with itemized canvases and reliefs that represented the departed’s life, their accomplishments, and strict ceremonies. The utilization of progressive scale — where more significant figures were portrayed as bigger — was normal in these fine arts.
- Funerary Art: The production of funerary things, for example, canopic containers, stone coffins, and ornaments was integral to Egyptian Old Workmanship. The renowned brilliant cover of Tutankhamun is one of the most amazing known instances of Egyptian funerary craftsmanship, representing the pharaoh’s heavenly status.
Mesopotamian Art: The Cradle of Civilization
The old locale of Mesopotamia, frequently alluded to as the “support of development,” was one more significant center for Antiquated Craftsmanship. The craft of Mesopotamia was different, mirroring the different societies that flourished in the area, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians.
- Cylinder Seals: One of the novel commitments of Mesopotamian craftsmanship was the chamber seal, a little tube-shaped object cut with pictures and composed. When moved onto dirt, the seal would have a consistent impression, frequently portraying scenes of love or folklore.
- Ziggurats and Architectural Reliefs: The amazing design of Mesopotamia is exemplified by ziggurats, layered sanctuary structures committed to divine beings. Improving reliefs decorated royal residences and portrayed the tactical victories and strict ceremonies of rulers.
- Sculpture and Statues: Mesopotamian mold went from the practical to the theoretical, with striking models including the sculptures of Gudea, a Sumerian ruler, and the lamassu, enormous winged animals with human faces that protected castle doors.
Greek Art: The Pursuit of Perfection
Old Greek workmanship addresses a critical crossroads throughout the entire existence of ancient art, where the human structure turned into a focal concentration. Greek craftsmen made progress toward authenticity and glorified excellence, bringing about the absolute most celebrated figures and engineering accomplishments.
- Sculpture: The Greeks culminated the specialty of chiseling the human body, making exact sculptures that praised actual excellence and physicality. Works like the Discobolus (Plate Hurler) and the Venus de Milo embody this quest for flawlessness.
- Pottery: Greek stoneware was practical as well as filled in as a material for narrating. Dark figure and red-figure ceramics strategies took into account point-by-point portrayal of fanciful scenes and day-to-day existence.
- Architecture: Greek engineering, especially the utilization of sections (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian orders), impacted Western building customs. The Parthenon, committed to the goddess Athena, remains a magnum opus of old Greek workmanship and engineering.
Roman Art: A Blend of Cultures
The craft of old Rome was acquired intensely from the Greeks yet in addition presented its developments, making a particular style that mirrored the realm’s huge and various domains. Roman Old Workmanship was a mix of authenticity and optimism, used to celebrate sovereigns, honor triumphs, and embellish public spaces.
- Sculptural Portraiture: Roman specialists were known for their practical busts and sculptures that caught the resemblance and character of their subjects. These figures frequently depicted heads, military pioneers, and significant residents.
- Mosaics and Frescoes: The Romans idealized the specialty of mosaic production, utilizing it to enhance floors and walls in homes, showers, and public structures. Frescoes, frequently portraying legendary or verifiable topics, were normal in well-off families.
- Architecture and Engineering: Roman design, like the Colosseum and water passages, exhibited creative expertise as well as designing ability. The utilization of curves, arches, and cement is considered the development of fabulous designs that have persevered for centuries.
Ancient Asian Art: Spirituality and Symbolism
Asian civic establishments, including those of China, India, and Japan, contributed altogether to the advancement of ancient art, accentuating otherworldliness, nature, and imagery in their imaginative articulations.
- Chinese Art: Old Chinese craftsmanship incorporates calligraphy, ceramics, bronze projecting, and painting. The Earthenware Armed Force, an assortment of life-sized figures covered with the primary Sovereign of China, Qin Shi Huang, is a momentous illustration of Chinese funerary craftsmanship.
- Indian Art: Craftsmanship from antiquated India is frequently connected to strict customs, especially Hinduism and Buddhism. Models and sanctuary carvings frequently portray divine beings, sacrosanct creatures, and scenes from legends like the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
- Japanese Art: The specialty of antiquated Japan, for example, the early Jomon earthenware, is described by its refined craftsmanship. The presentation of Buddhism likewise affected the improvement of Japanese Antiquated Craftsmanship, prompting the making of Buddhist sculptures and sanctuary designs.
The Techniques and Materials of Ancient Art
Making Old Workmanship required authority of different strategies and the utilization of various materials, contingent upon the locale and period.
- Stone Carving and Sculpting: Stone, being a strong material, was regularly utilized for figures and building designs. The Egyptians utilized limestone and rock, while the Greeks favored marble for its fine grain.
- Bronze Casting: Bronze was utilized to make sculptures, weapons, and instruments. The lost-wax projecting procedure permitted antiquated craftsmen to create perplexing metalwork, like the bronze sculptures of the Greeks and the ceremonial vessels of the Chinese.
- Painting and Pigments: Early painters utilized normal shades from minerals and plants to make clear tones. Procedures like fresco painting considered the enrichment of walls and roofs, as found in Roman estates and Egyptian burial chambers.
- Pottery and Glazing: Earthenware making was one of the earliest artistic expressions, with strategies developing to incorporate coating, which added variety and strength to the vessels.
The Legacy of Ancient Art in Modern Times
The impact of ancient art can in any case be seen today, in galleries and archeological destinations as well as in present-day workmanship and engineering. Old strategies, themes, and styles have been resuscitated and rethought by contemporary craftsmen, fashioners, and modelers, guaranteeing that the tradition of antiquated workmanship keeps on moving to new ages.
Present-day creative developments, for example, neoclassicism drew intensely from the style of old Greece and Rome. Moreover, the imagery found in old Egyptian and Asian workmanship has impacted current craftsmanship developments like oddity and unique workmanship.
Conclusion
Old Workmanship is a demonstration of the resourcefulness, innovativeness, and social extravagance of early developments. From the cavern compositions of ancient people to the great models of traditional relics, antiquated craftsmanship has been the embodiment of human articulation since the beginning of time. Its immortal nature lies in its tasteful allure as well as in its capacity to convey stories, convictions, and feelings from a long time ago. As we proceed to study and respect these old works of art, we gain a more profound comprehension of our common human legacy and the getting-through force of craftsmanship.
In investigating the excursion of ancient art, we can see the value in its enduring effect on current culture, as its subjects, methods, and materials keep on reverberating across societies and times. To be sure, the universe of ancient art is an immortal excursion that eternity improves how we might interpret the past, present, and future.
Read More>> CFBWH: In-Depth Information